Structural Assessment and Remediation of Plaza Level Slab
Overview
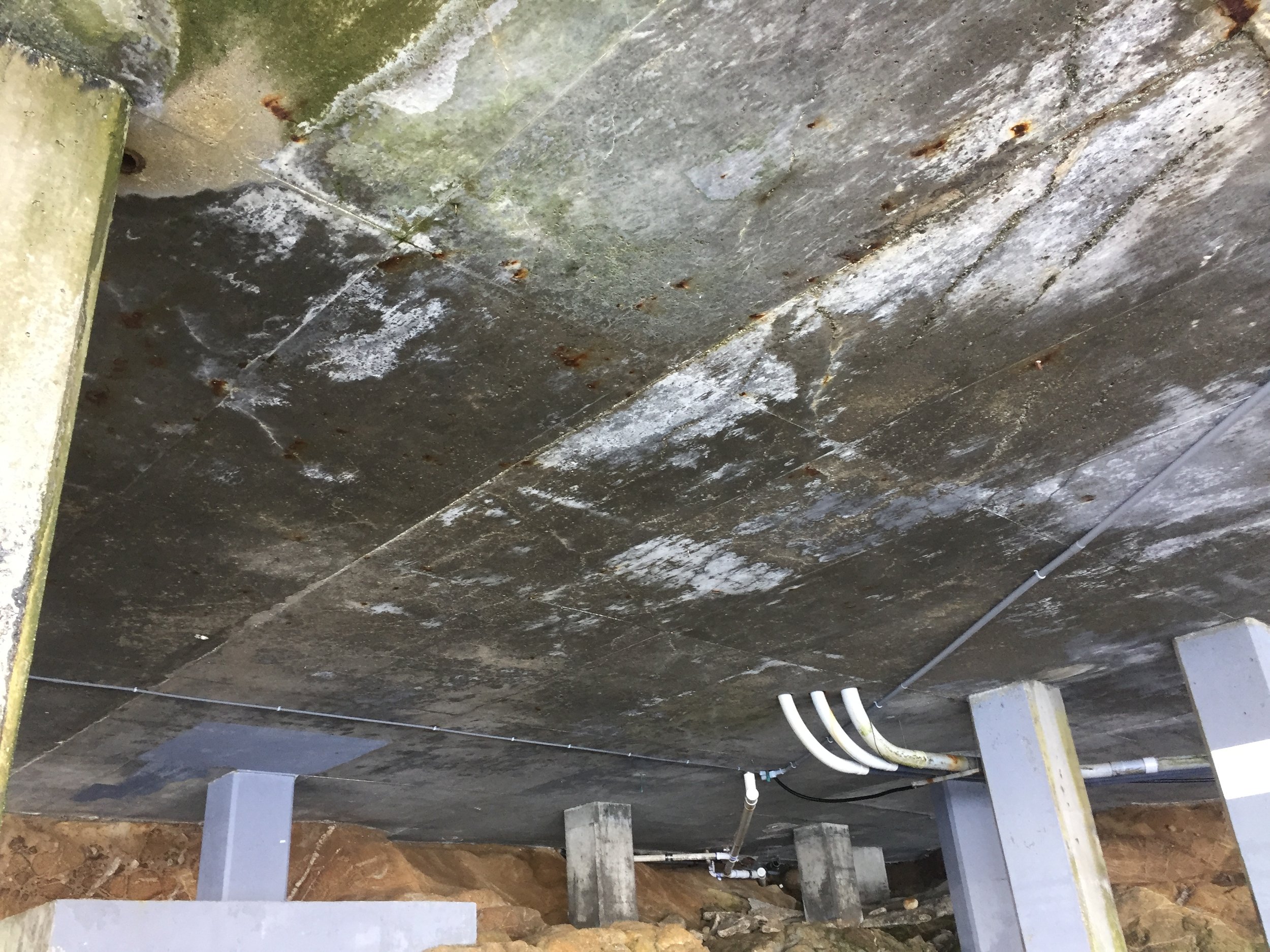
An historic coastal hotel required an in-depth structural assessment of its reinforced concrete plaza-level slab due to visible distresses, including excessive deflection, cracking, delamination, and corrosion. These issues raised concerns about the slab's long-term structural integrity, prompting hotel management to seek a professional evaluation. Given the hotel's exposure to a harsh marine environment, the potential for accelerated deterioration was a critical factor in the assessment.
Concrete Science® conducted an extensive investigation to determine the extent of deterioration and identify appropriate remediation measures. Through a combination of nondestructive testing, material sampling, and structural analysis, the evaluation aimed to provide data-driven solutions to restore the slab’s integrity and ensure long-term stability. The findings and recommendations from this study formed the basis for targeted repairs and preventive maintenance strategies.
Scope of Work
The evaluation process incorporated multiple testing methodologies to assess the extent of concrete deterioration, reinforcement corrosion, and structural deficiencies. The investigation began with a comprehensive structural inspection, followed by nondestructive and destructive testing techniques to gather critical data on concrete strength, slab deflection, and corrosion activity. These assessments were crucial in determining the severity of structural damage and guiding remediation efforts.
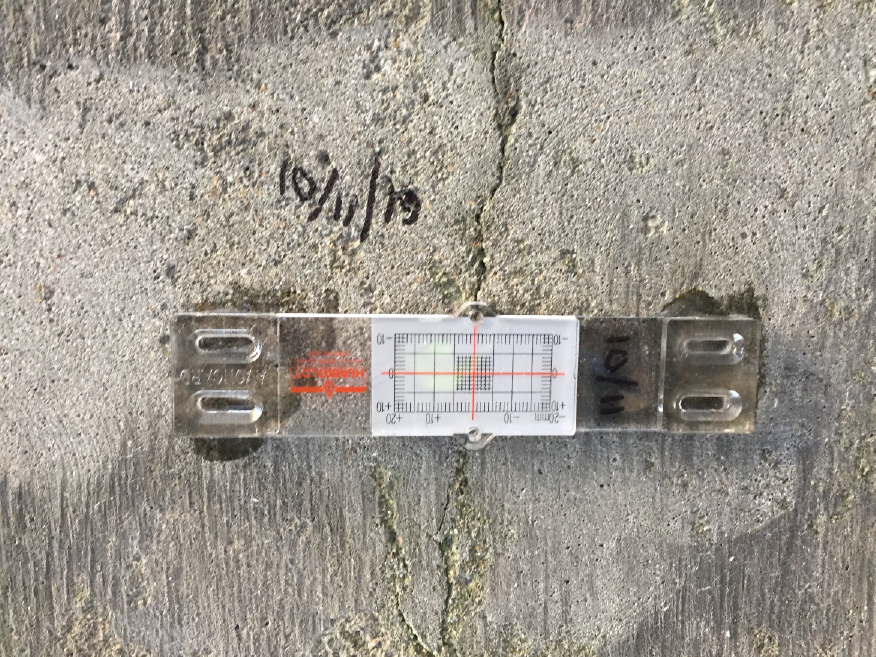
Installation of crack gauges to monitor ongoing crack movement and slab displacement.
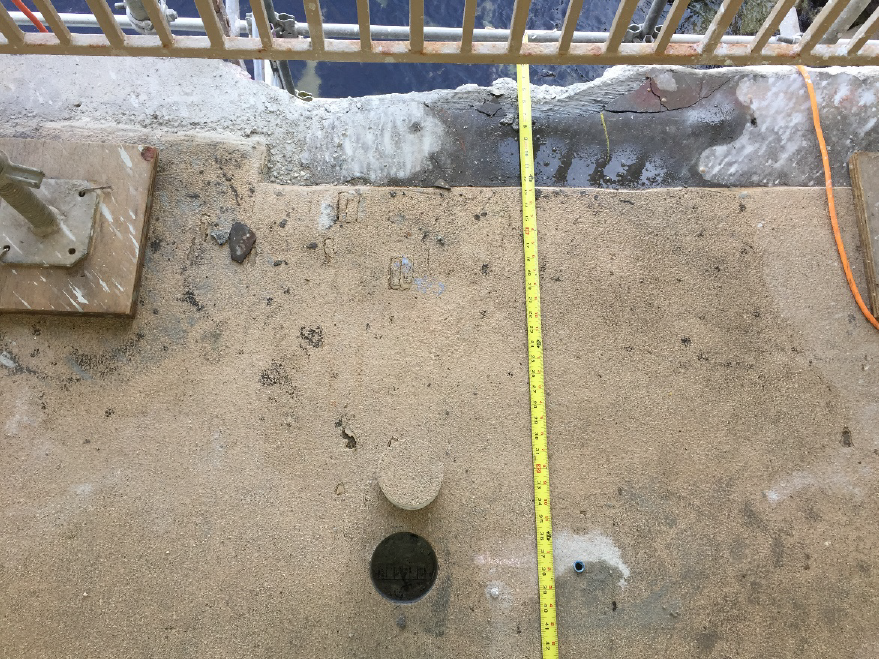
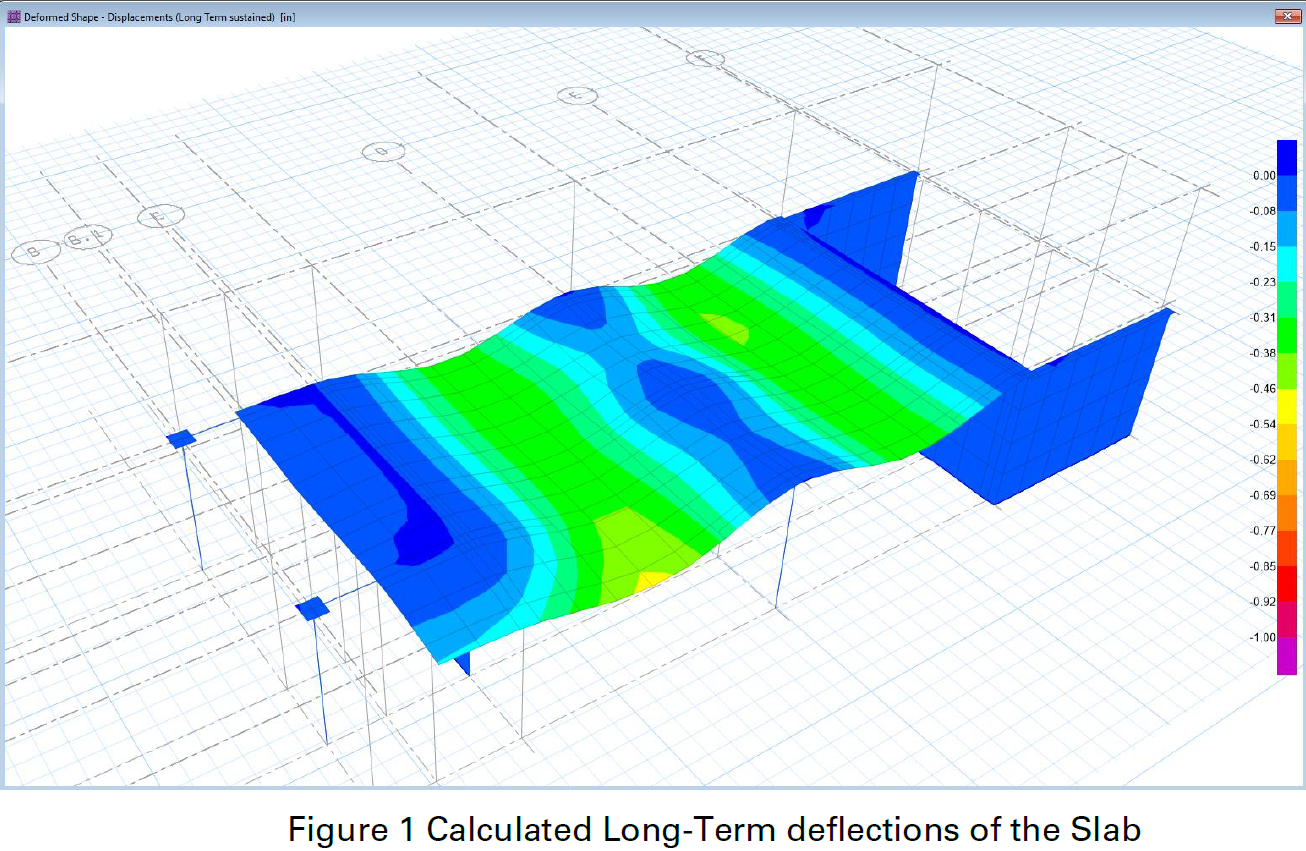
Level surveys from the soffit side to measure deflections and compare them to theoretical values.
A Finite Element structural analysis to evaluate slab performance under the long-term loads.
Rebound Hammer Testing: Nondestructive testing to estimate concrete compressive strength.
Acoustic Impact Echo Testing: Used to detect internal voids, delaminations, and slab thickness variations.
Half-Cell Corrosion Potential Testing: Assessed the probability of corrosion activity in steel reinforcement.
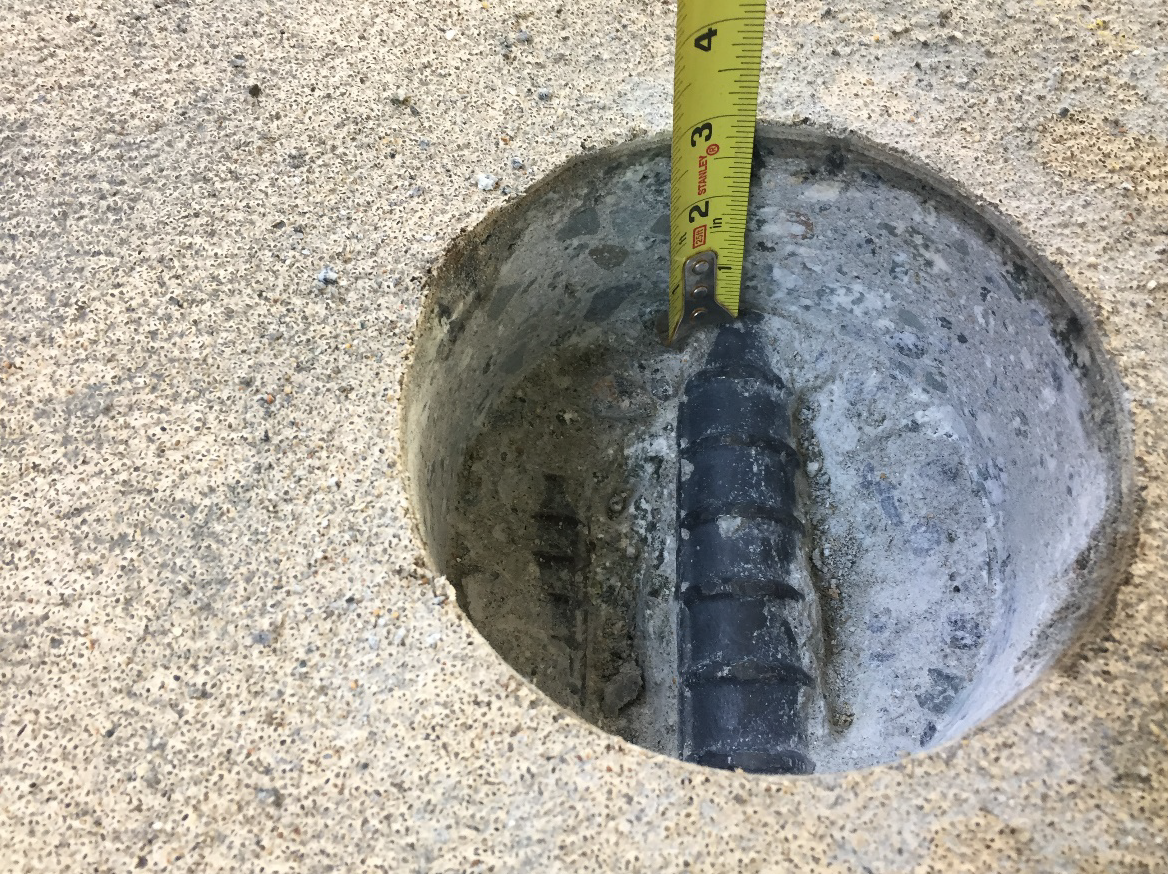
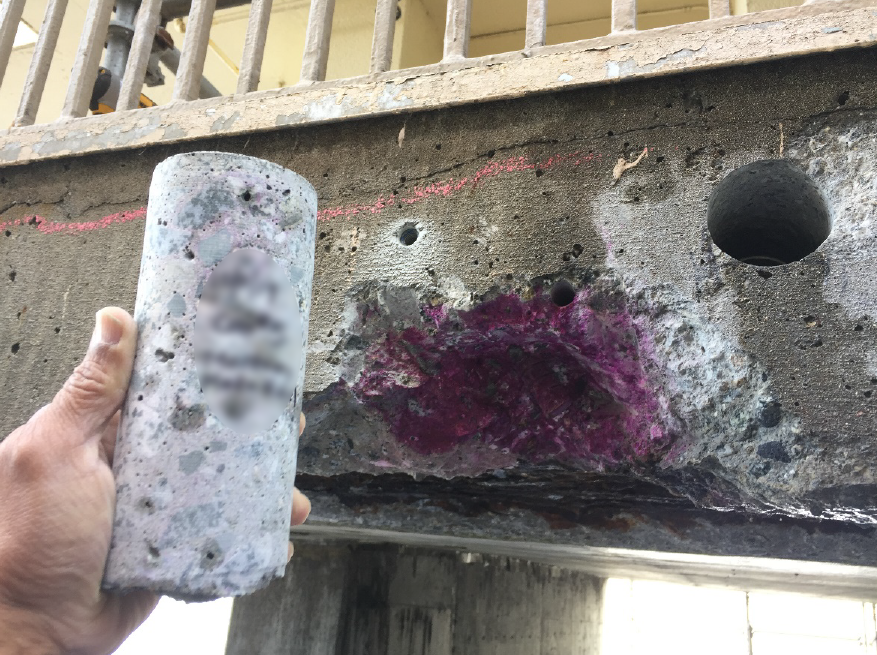
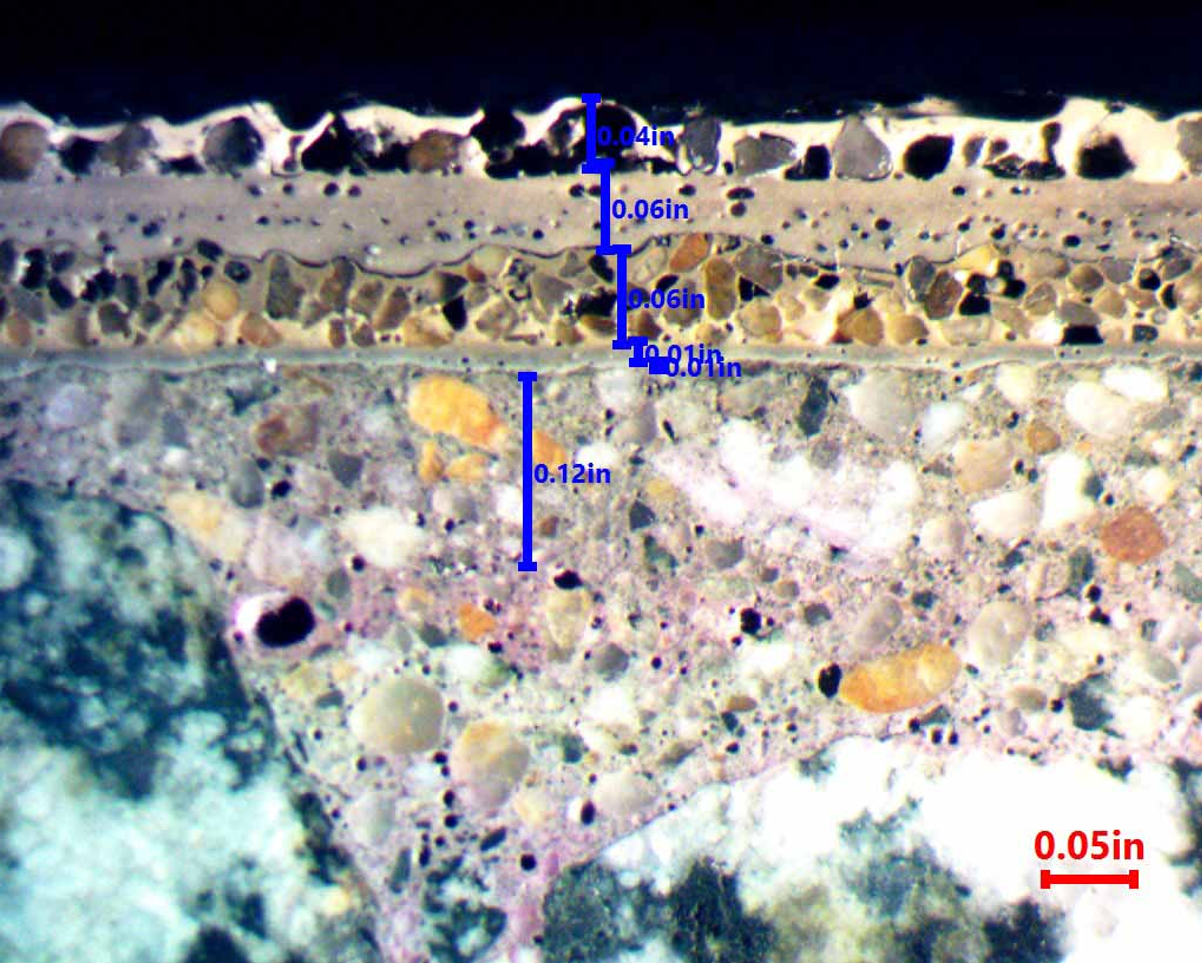
Concrete Core Sampling: Provided a direct assessment of reinforcement corrosion, compressive strength, and microscopic characteristics.
Acid Soluble Chloride Content Analysis: Determined chloride ion ingress, a major contributor to the reinforcement corrosion and deterioration.
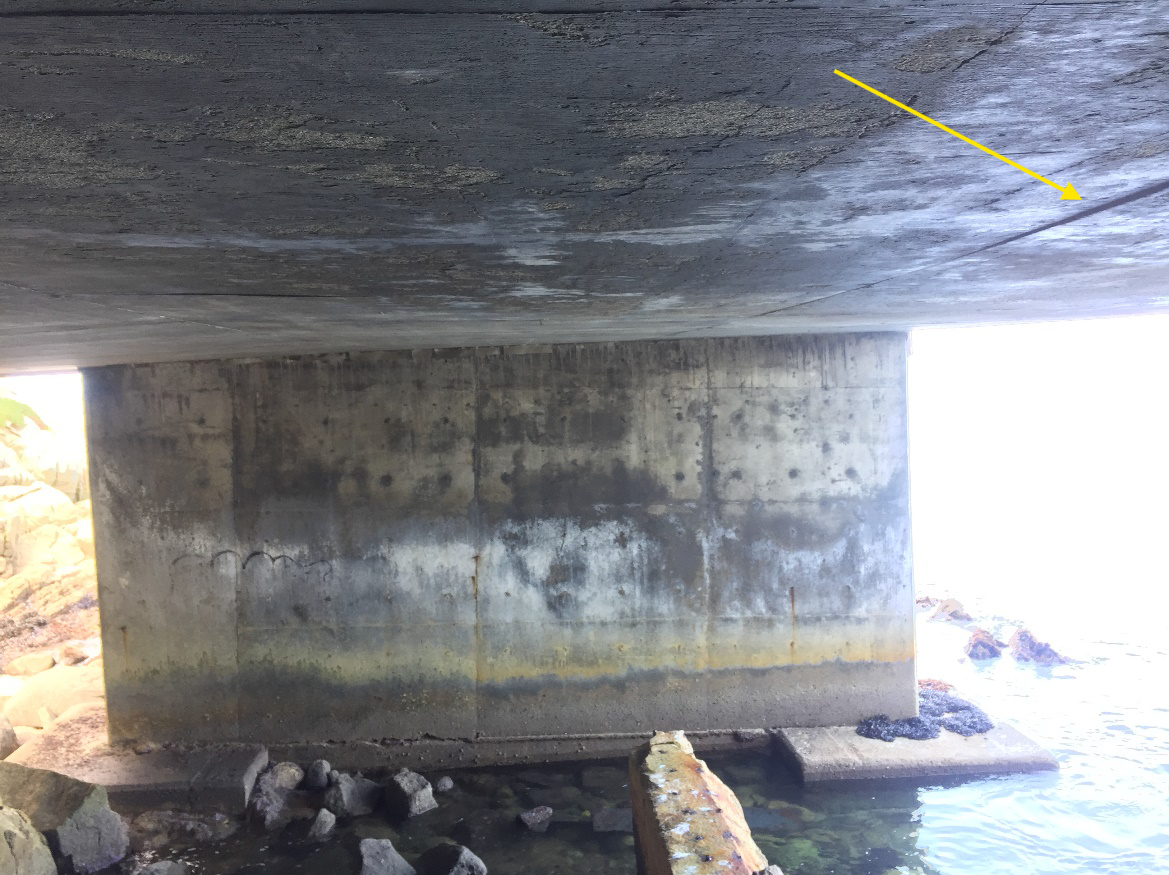
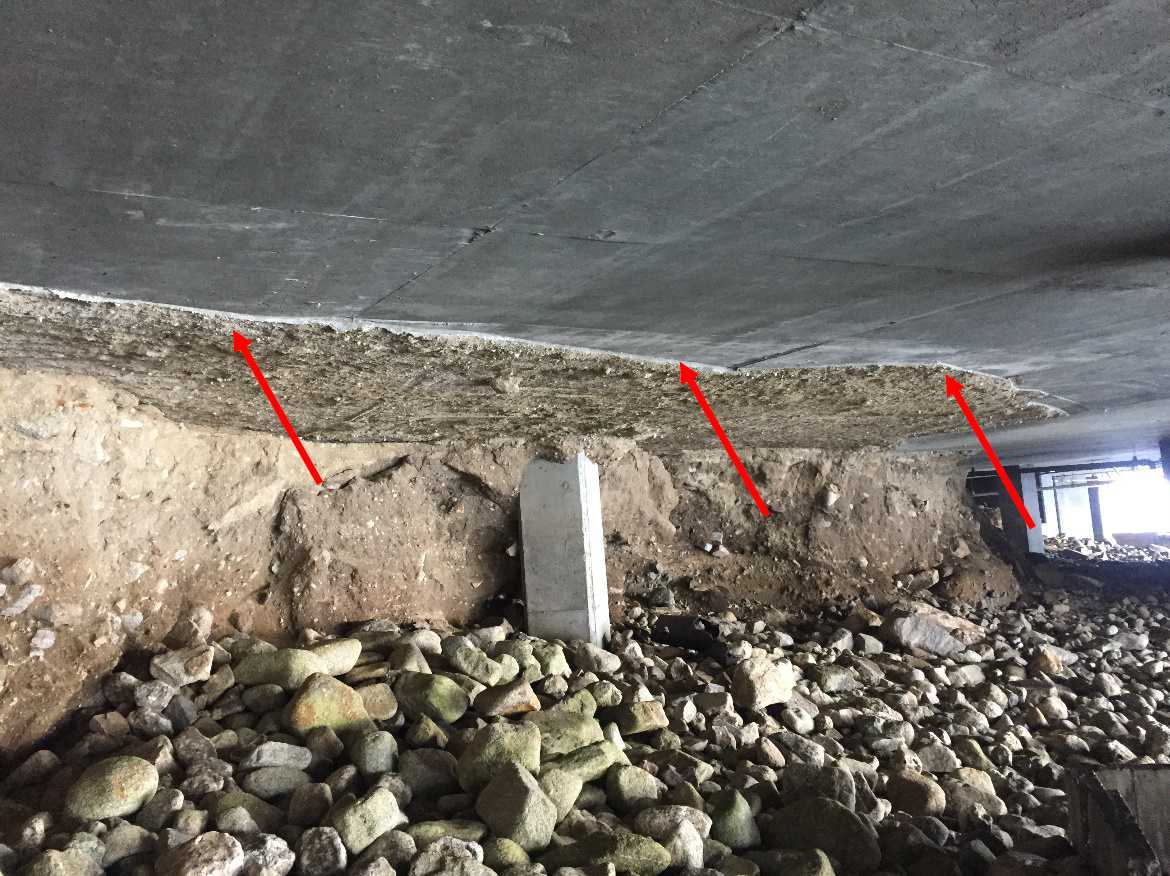
Evaluation of erosion patterns and soil loss at the foundation and plaza slab perimeter due to high tides and coastal exposure.
Recommendation of a geotechnical assessment to identify potential foundation stability risks and erosion mitigation strategies.
This comprehensive diagnostic approach allowed engineers to develop an effective concrete repair and corrosion mitigation plan, ensuring structural longevity and durability.
Key Findings
Excessive Slab Deflection and Structural Instability:
The expected long-term deflection due to creep and shrinkage was estimated at 0.4-0.5 inches.
Actual measured deflection exceeded theoretical values, suggesting potential construction-related deficiencies.
Severe Corrosion and Chloride Contamination:
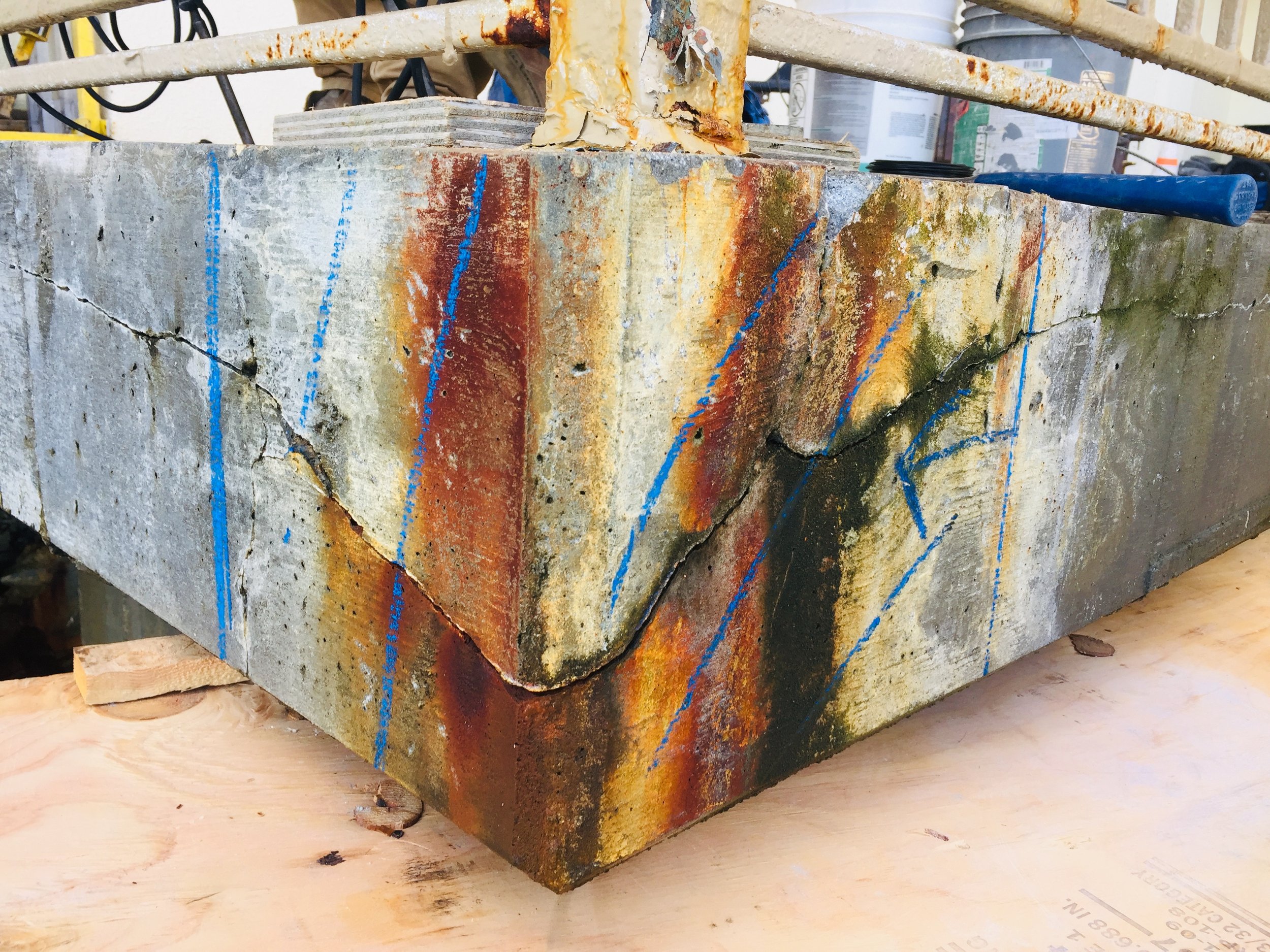
Chloride levels in concrete near slab edges exceeded the corrosion threshold (>1.5 lb/cu yd), primarily due to long-term exposure to salt-laden air.
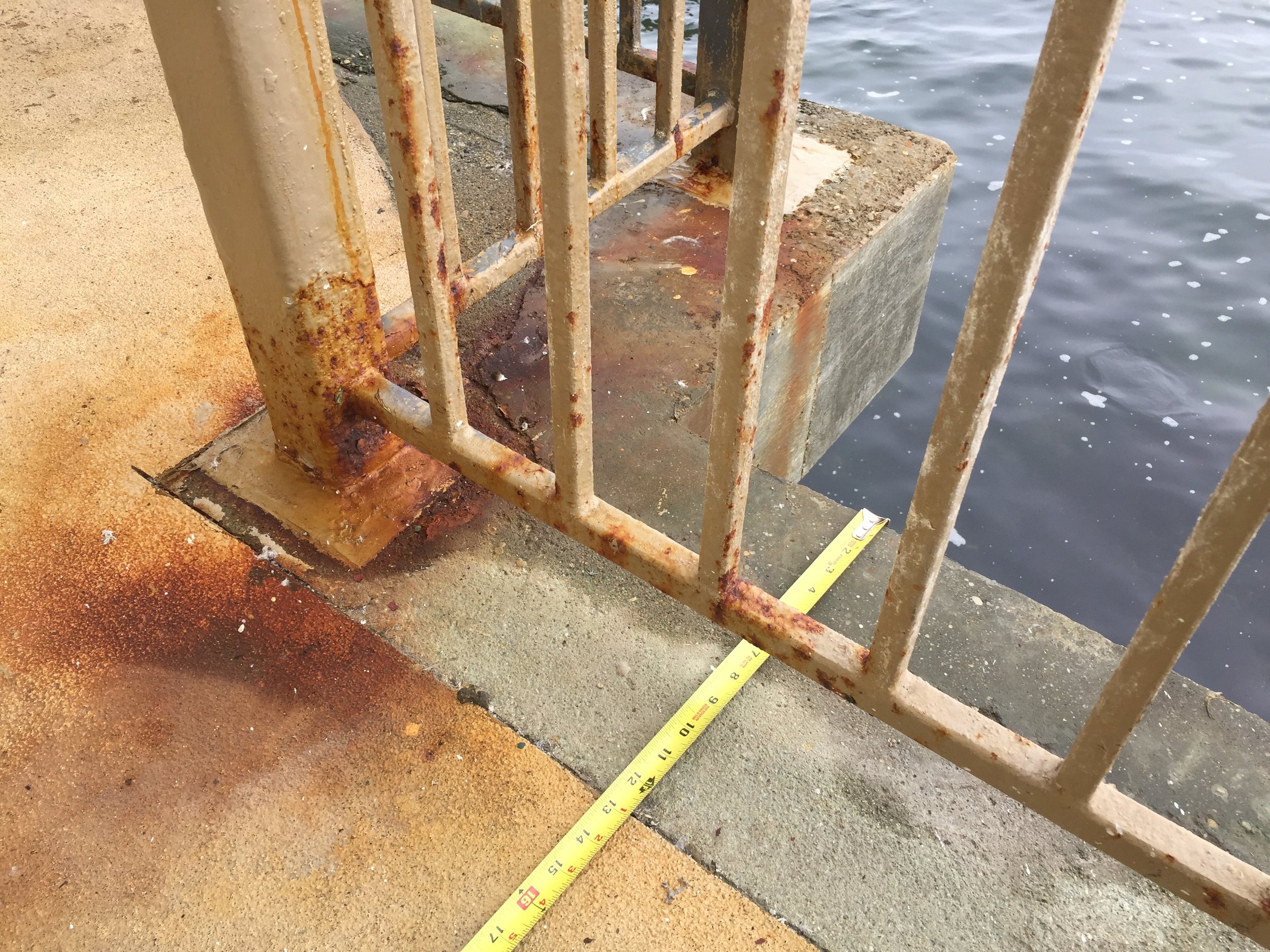
Significant reinforcement corrosion was detected at slab edges and railing post bases, leading to delamination and spalling.
Concrete Strength and Quality Assessment:
Nondestructive testing indicated an average compressive strength of about 4,500 psi.
Laboratory-tested core samples confirmed strength adequacy, averaging 5,730 psi.
Petrographic analysis verified well-consolidated concrete with an optimal water-cement ratio.
Foundation and Soil Erosion Concerns:
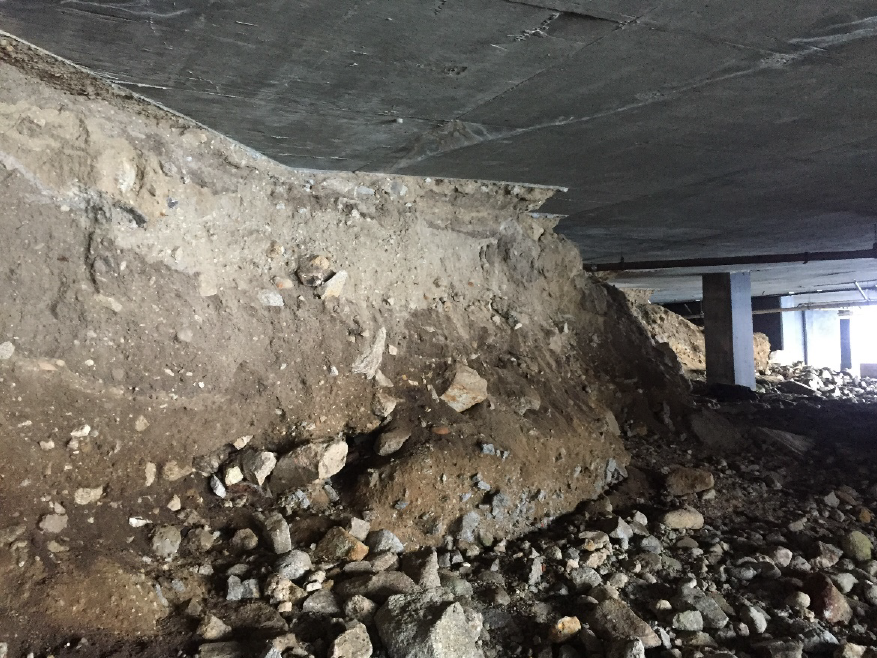
Observations revealed progressive soil erosion beneath the structure due to coastal high tide activity.
Potential risk to long-term foundation stability was identified, warranting further geotechnical evaluation.
Solutions and Recommendations
1. Immediate Structural Monitoring:
Conduct regular slab level surveys and crack gauge inspections.
Implement continuous reinforcement corrosion monitoring.
2. Targeted Concrete Repair and Corrosion Prevention:
Remove and replace delaminated concrete at slab edges.
Apply corrosion inhibitors and protective epoxy coatings to reinforcement.
Replace severely corroded railing posts with marine-grade corrosion-resistant materials.
3. Long-Term Structural Durability Measures:
Implement a waterproofing and anti-corrosion system to prevent further chloride ingress.
Apply high-performance sealer to exposed concrete surfaces.
4. Foundation and Soil Stabilization Strategies:
Conduct a comprehensive geotechnical investigation to assess foundation stability risks.
Develop and implement erosion control and soil stabilization techniques.
Outcome
The structural assessment and remediation plan provided a roadmap for restoring and strengthening the plaza level slab, addressing concrete deterioration, reinforcement corrosion, and foundation stability concerns. Targeted repairs, proactive corrosion mitigation, and long-term monitoring measures were implemented to ensure continued structural integrity and prevent further degradation. These interventions significantly improved the durability and resilience of the structure, reinforcing its ability to withstand coastal environmental stressors and extending its service life.